Startup refers to a business that is just getting started. Startups are created by one or more business owners who desire to provide a good or service they feel there is a market for. These businesses typically have large startup expenses and little income, which is why they seek funding from a number of sources, including venture capitalists.
Startups are often funded by the founders, who may also make attempts to secure outside funding before they take off. Family and friends, venture capitalists, crowdfunding, and loans are a few examples of financial sources. Startups also need to think about their legal structure and the location of their operations. Startups have a significant risk because failure is highly likely, but they may also be very special workplaces with fantastic benefits, a focus on innovation, and excellent learning opportunities.
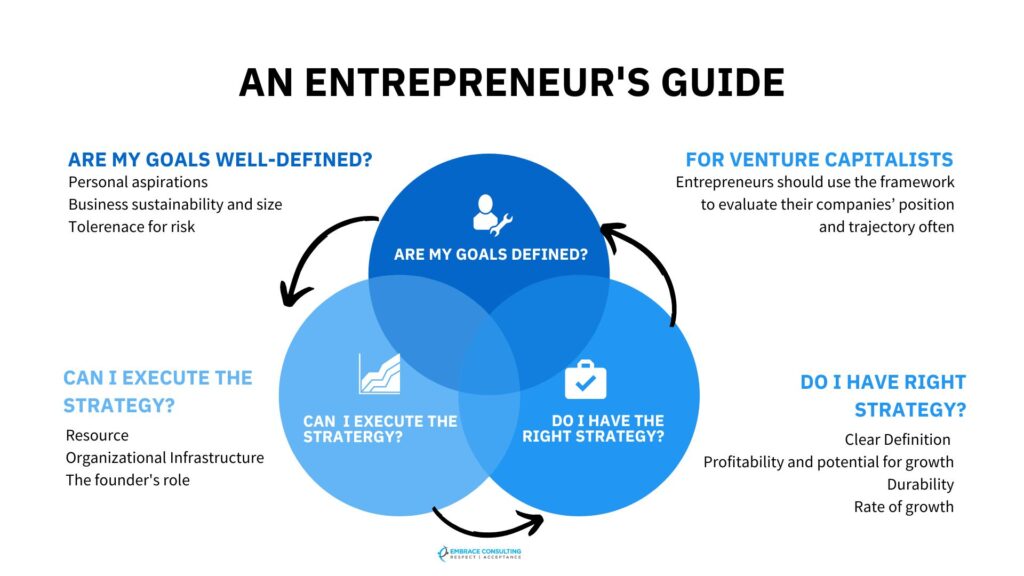
In order to grow enterprises, entrepreneurs can utilize a framework developed by the Harvard Business Review. A series of three questions make up the framework. The first phase helps entrepreneurs define their current goals, the second assesses their plans for achieving those goals, and the third enables them to gauge their ability to carry out their plans. Due to the questions’ hierarchical structure, business owners must first address the fundamental, overarching issues before focusing on details and improvements. This strategy does not prescribe a one-size-fits-all formula for success because it does not imply that all businesses or all entrepreneurs develop in the same way.
Compass for Entrepreneurial Strategy
An individual’s strategy is based on the understanding that a go-to-market plan for every invention necessitates decisions regarding which clients to target, what technologies to use, what organizational identity to adopt, and how to position the business in relation to which competitors. Following are some of the strategies used by various businessmen across their start-ups:
1.The Strategy for Intellectual Property
The company works with established players in this sector of the economy while maintaining control over its technology or product. The start-up concentrates on developing ideas while avoiding the expenses of activities that are customer-facing and further down the supply chain. The audio business Dolby serves as an excellent example.
2.The Strategy of Disruption
It entails choosing to engage in direct competition with market leaders, placing more emphasis on the idea’s commercialization and quick market share increase than on maintaining control over the idea’s advancement. For example, Netflix used the strategy of disruption to promote a successful business plan.
3. Value Chain Strategy
The excitement of disruption is unlike the dullness of a value chain strategy. Instead of policing the new product and building entry barriers, the start-up invests in commercialization and ongoing competitive strength, but its main goal is to integrate into the current value chain as opposed to upending it. For example, by acting as a value-added addition to conventional stores, Peapod rose to become the top online grocer in the United States.
4.Architectural strategy
Entrepreneurs who pick and thrive with an architectural plan typically have extremely high public profiles, in contrast to the value chain strategy, which is the territory of quiet achievers. Although it is out of reach for many, if not most, concepts and extremely hazardous when it is possible, this technique enables start-ups to compete and gain control. Google and Facebook rule this space. A restaurant reservation service online called OpenTable is a classic example of this strategy.
To conclude, the risk involved in starting a business is neither eliminated nor reduced by the entrepreneurial strategy compass. It offers a logical foundation for getting away from the apparent facts of the current world and defining potential new surroundings to pick from. The framework is intended to guide the founder’s imagination and commitment towards the realization of their ideas and assist individuals in making the right decision.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————–
India’s startup funding slides 68% after Tiger and Soft Bank make virtually no deals.
Manish Singh | June 29, 2023
In the first half of 2023, Indian startups have experienced a significant decline in funding, with late-stage backers reducing investments due to a slowdown in the broader public market. Unlike the previous years, 2023 has not seen the emergence of any new unicorns in the Indian startup landscape. Despite the setback, Indian startups still have potential opportunities with the substantial “dry powder” of untapped capital reserves held by venture capitalists. Active VC firms in India have secured new and larger funds in the past 18 months, indicating the potential for increased investment activity in the coming months. While valuations for some startups have faced downward adjustments, there remains optimism that rational investment practices will prevail, leading to increased deployment of capital in the next couple of years.
Growing tech dependency can both help and hinder DEI, needs constant monitoring: Hexaware’s Gwen Kolader
Mamta Sharma | 8th June 2023
Technology plays a crucial role in advancing diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) within organizations, breaking down barriers and fostering equality. However, it must be acknowledged that unchecked, technology can inadvertently perpetuate biases and discrimination. Hexaware Technologies focuses on employee and customer happiness through diversity and inclusivity. Specific technologies include AI tools for objective hiring, language analysis tools to detect bias, and AR/VR for empathy. Analytical platforms and accessibility-focused technologies are also important. AI can reduce biases by promoting objective decision-making and personalized training. However, potential pitfalls include inherent biases in AI tools and misuse by users. VR and AR enhance empathy across cultural backgrounds. Ethical concerns involve data privacy, fairness, accessibility, transparency, and adverse effects. To measure effectiveness, diversity at all levels, participation in DEI training, fair evaluations, customer satisfaction, transparency, and input are crucial.












